Can You Drive An Electric Car Through Water?
The emergence of electric vehicles is probably one of the most critical steps taken to reduce emissions and help stop climate change. There is still work to do, including making them accessible for citizens of poorer countries. There are also detractors, many of whom are spreading false information about the safety of electric cars.
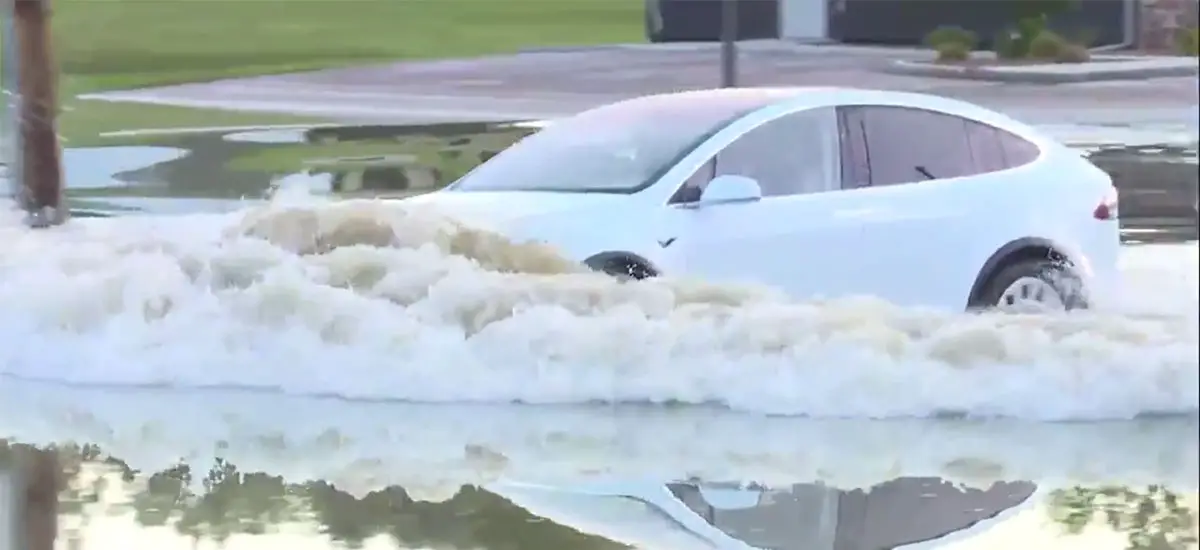
EVs can drive through water. However, when an Electric Vehicle’s battery is placed in fresh water to a depth of one meter for 30 minutes, water should not enter. The battery is installed on the bottom of the EV; this increases the ability to stay upright if carried away in floodwaters.
There is much fake news about electric vehicles, such as the danger of being electrocuted if the car drives through water, or a massive short circuit will occur, and the car will not function in water. The reality is somewhat different, as we explain in this article.
Table of Contents
- Electric Vehicles Can Be Driven Through Water
- EVs Can Drive In Water Better Than Conventional Vehicles?
- Conclusion
Electric Vehicles Can Be Driven Through Water
There’s a lot of misinformation concerning the dangers electric cars present, particularly regarding water damage.
There is a lot of fake news that electric vehicles present higher risks for fire and rescue crews of being electrocuted if they force entry into the car and inadvertently cut the wiring at the scene of the accident or flood.
While any machine which uses electricity does present the danger of electrical shorts if the wiring is compromised, the rumor mill vastly overinflates the risks associated with electric vehicles.
There hasn’t been a single case recorded of a rescuer being shocked while extricating someone from a crashed electric vehicle, whether it was underwater or not.
EVs must pass all the regulatory requirements that internal combustion engine-powered cars meet to be certified as roadworthy. They must also meet specific rules that ensure the electrical components present no more significant risks to anyone.
To ensure the vehicles meet these regulatory requirements, they must provide the following.
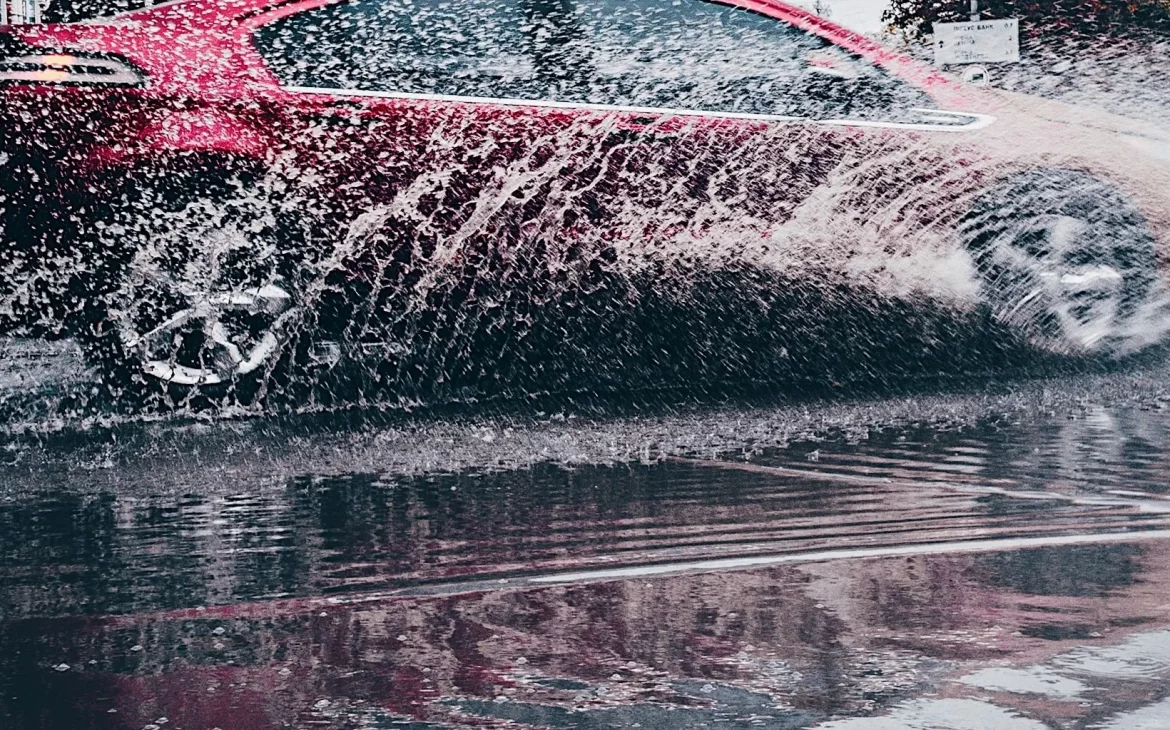

Driving Through Water Must Not Damage The Electric Vehicle
In an accident, the batteries must not pose a fire or electrocution risk.
The installation must physically restrain the battery in an impact-resistant cage that can survive high-impact forces. Electric Vehicle battery packs are encased in a sealed metal shell electrically isolated from the rest of the car.
The shell is usually covered in carpet or an interior panel. If the body’s metal gets wet, it is designed to resist corrosion.
If the electric vehicle experiences a high g-force, the battery must automatically shut down and isolate itself from the car.
Lithium-ion batteries are vulnerable to overheating, which can cause a runaway thermal event and cause massive fires or explosions in extreme cases.
Regulations require that the design of the space between the Lithium-ion battery cells must prevent neighboring cells from overheating if a cell is damaged and starts to overheat.
The nickel-metal hydride batteries used in hybrids and electric cars are maintenance-free sealed cells, so nothing gets in or out.
The Battery Remains Fully Sealed If Driven Through Water
Lithium-ion batteries are designed to be maintenance-free, and nothing gets in or out of the batteries.
Electric vehicles are required to conform to the standard IP67. IP is derived from the international IEC standard 60529and stands for Ingress Protection.
The following numbers relate to the battery’s ability to prevent ingress from solid and liquid contaminants.
The first number, “6,” is the score the battery must achieve to withstand ingress from particles as small as dust, and therefore the Electric Vehicle battery must be completely dustproof. It means that dust cannot enter the crevices and therefore cannot damage or soil it internally under any circumstances.
The second number, “7,” is the score of the Electric Vehicle’s battery’s ability to withstand ingress from freshwater. In this case, the object must completely prevent water from entering up to a depth of 1 m for 30 minutes.
In the improbable scenario where water may get into the shell of a lithium-ion battery, there’s are still more defenses.
The cells that make up a Lithium-ion battery used in electric cars are sealed, so nothing gets in or out. The gel formed between the cells prevents any cross-over of the contaminate or so even spillages won’t happen if the batteries are ruptured in a crash.
The high-voltage cabling needed to transport the 200 – 300-volt current is similarly protected and insulated.
In terms of an Electric Vehicle being driven in water, there is less chance that an electric car will fail than a car powered by an internal combustion engine.
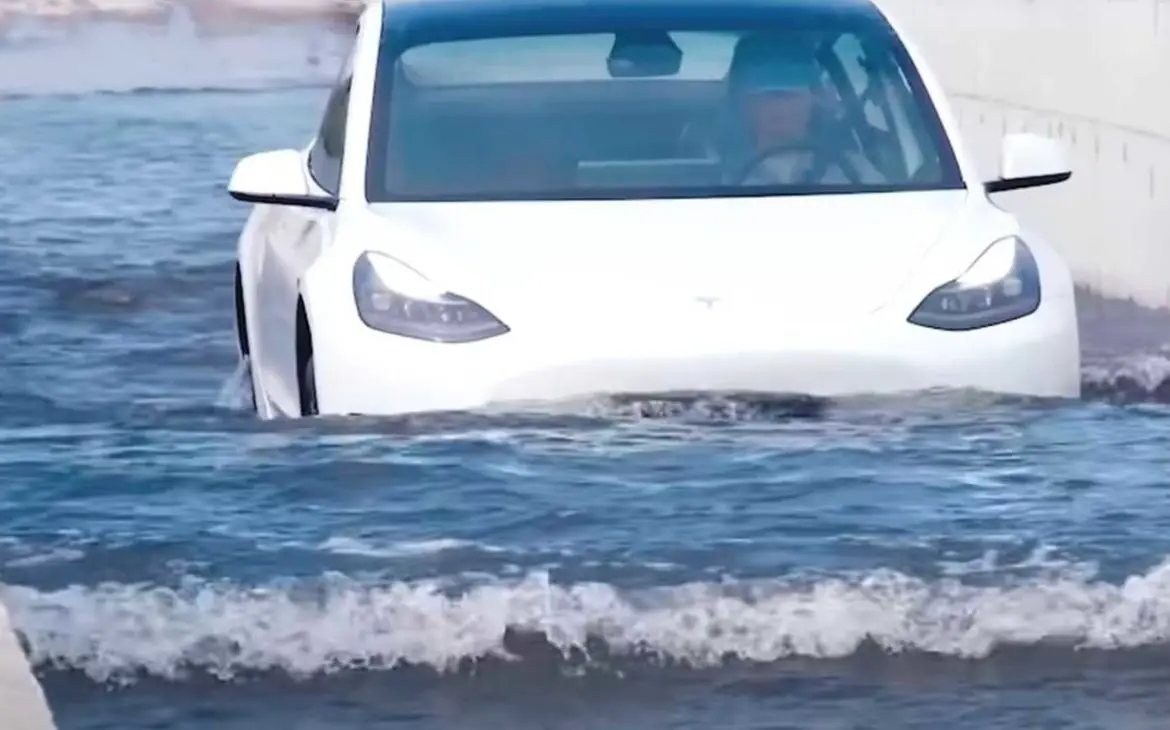

The Electric Cars Pass The Euro NCAP Assessment
(NCAP) which stands for the “European New Car Assessment Programme,” is a scoring system where vehicles are subjected to standardized collision tests. The Euro NCAP evaluated rating is calculated on a scale of 1 – 5.
All EVs are subject to the Euro NCAP assessment; There are four collision tests which include
- A full-frontal collision
- A front offset collision
- A side-impact collision
- A side impact into a pole.
These tests ensure that the vehicle’s strong structures, extensive crumple zones, and multiple airbags protect everyone.
EVs Can Drive In Water Better Than Conventional Vehicles?
Although no manufacturer would say it is a recommended activity to drive their product through water, the reality is that electric vehicles offer more protection against water damage than conventional vehicles.
Internal Combustion Powered vehicles require holes to transfer air to the engine and exhaust gasses out of the back.
Electrical ignition systems are installed close to the carburetor or fuel injection systems, which are not sealed from water ingress. It makes these systems vulnerable to water damage.
Fuel tanks can rupture or crack, potentially causing fires or, at the very least, water contamination of the gas.
On the other hand, regulations force electric vehicle manufacturers to seal all the electrical systems from any external contaminants. As a result, Electric vehicles tend to float on the water’s surface rather than sink.
Having the batteries installed at the bottom of the car means electric vehicles have their weight low, making them less likely to overturn in flood water than a conventional vehicle.
Conclusion
Can you drive your electric vehicle into the water? The answer is you can, and depending on the ferocity of the water current, the electric car should cope.
Despite this, it is strongly advised that you never drive an electric vehicle into the water as a deliberate act unless forced to in an emergency.
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.