Can Tesla Cars Explode?
Whenever a new technology or shift in the way things have been done is introduced, there is often resistance or pushback from people uncomfortable with change. Before Tesla’s incredible rise to the most valuable motor manufacturing company in the world, this resistance was genuine.
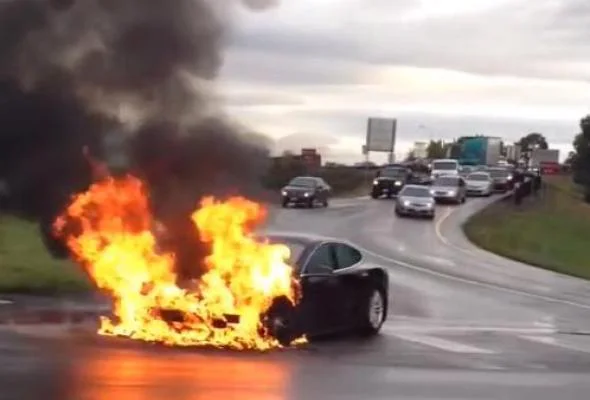
EVs, mainly Tesla’s, are very safe, and the chance of exploding is minimal. Sixty Tesla Cars have been damaged by fire in the last eight years. That means, every year, 7.5 Tesla’s have been damaged by fire, compared to an average of 212,500 vehicle fires overall.
In the early days, Tesla owners faced a lot of flack from conventionally powered vehicle drivers. Parking garages tried to ban Tesla’s; social media spread fake news about Tesla’s spontaneously combusting, and Lithium-Ion EV batteries were involved in fire events.
Table of Contents
- Are Tesla Cars Prone to Exploding?
- Why Do Some Tesla Cars Explode?
- How Does Tesla Prevent an Explosion from Happening?
- Conclusion
Are Tesla Cars Prone to Exploding?
All EVs use Lithium-ion batteries as the primary power source. Lithium-ion batteries have advantages over all other types of batteries.
- They are much lighter
- They last at least 20 years
- They can be discharged to a lower percentage than gel or lead-acid batteries.
- Relatively low self-discharge than other batteries
- Low Maintenance
The disadvantages of Lithium-ion batteries are:
- They are not as robust as other batteries and require protection from being overcharged and discharged too far.
- The protection installed in the batteries includes a physical structure to stop the heat spreading and electronic safety systems.
- There have been instances where early versions of Lithium-ion batteries have spontaneously burst into flames.
The problems create a possible situation where an explosion could occur.
Why Do Some Tesla Cars Explode?
Tests of the early version of batteries proved that if the temperatures were increased to more than 266 degrees Fahrenheit (130 degrees Celsius), the batteries burst into flames, causing a chain reaction through the whole battery pack.
The highest temperature recorded in these tests was 1,472 degrees Fahrenheit, and the subsequent explosion sent the remaining skin of the battery rocketing into the sky.
This chain reaction is called a thermal runaway.
Although the number of incidents has been statistically irrelevant, there have been cases where Teslas have burst into flames for no apparent reason. Some examples of these vents are:
- In 2013 a Tesla burst into flames after being involved in an accident in Washington State.
- Again in 2013, a Tesla combusted after being involved in an accident in Merida, Mexico.
- In 2016 a Tesla was being driven on a promotional drive when it burst into flames.
- In 2017 in Lake Forest, California, a car burst into flames after an accident.
- In 2018 an eighteen-year-old driver was killed during an accident that caused the car to immolate.
- In 2019 a Tesla spontaneously combusted in a parking garage in Shanghai.
- In 2021, while driving in Berkley, California, just three days after taking delivery of his new Tesla, a customer reported that his car burst into flames for no apparent reason.
In 2021 there were five fire-related incidents and one incident in 2022.
Tesla has sold 1.91 million EVs since the launch of the first Roadster.
A Tesla catching fire is a dramatic event easily used as headlines by a lazy or adversarial press. The reality is that only 60 Tesla fires have been reported worldwide; this means that only 0.000031414% of Tesla’s have been involved in fire incidents globally.
There are an annual average of 212,500 vehicle fires in the United States alone. In America, there are approximately 263 million cars registered; this means that there is a 0.08% chance of a vehicle powered by an internal combustion engine bursting into flames (As opposed to Tesla’s minimal 0.000031414% chance.)
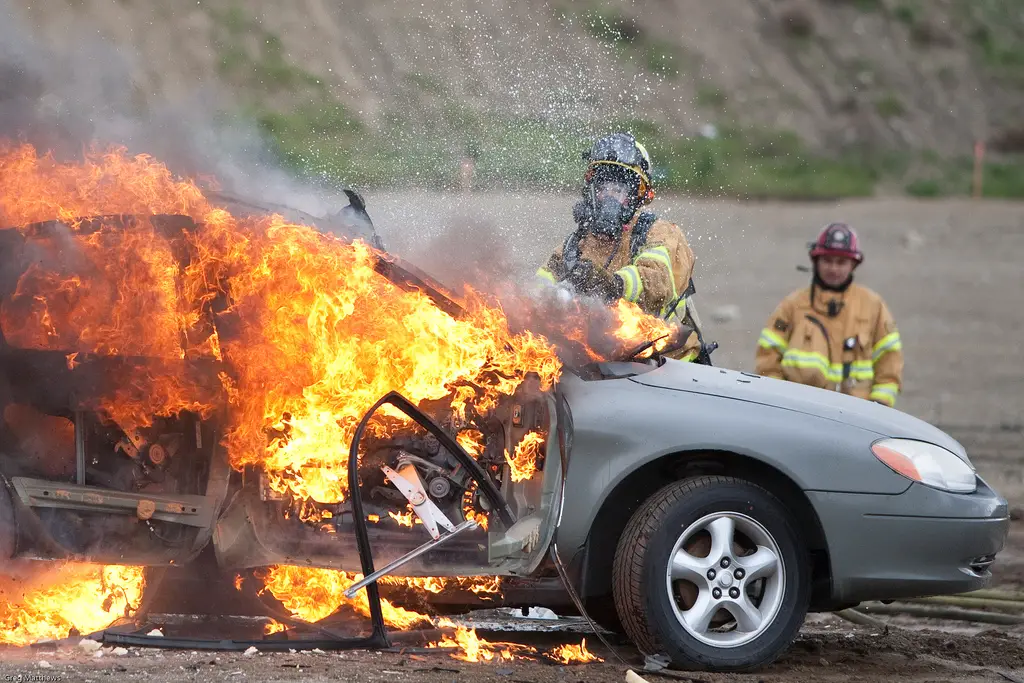

How Does Tesla Prevent an Explosion from Happening?
Tesla employs several precautions to ensure their vehicles do not explode. These include
The 1st Measure is the Design of the Lithium-Ion Battery
Early model Tesla cars had 7,000 Lithium battery cells in a single vehicle; this had the potential of creating a massive fireball and explosion. The company needed to find a solution.
If this had happened in an EV carrying passengers, the results would have been catastrophic and probably closed the EV manufacturers and possibly destroyed the entire industry.
Tesla’s solution is to line up each cell a few millimeters apart, insert a tube of advanced phase-change materials that absorb heat between them, and finally, cover all the cells with a batter-like mixture of minerals, reducing the heat transfer properties.
If a damaged or defective cell does begin to overheat, its energy is dissipated to the rest of the battery cells, and no individual cell should ever reach combustibility.
The 2nd Measure is the Physical Protection of the Battery
Tesla batteries are installed in a crash-resistant frame designed to withstand high-energy impacts; this is intended to stop the Lithium-Ion battery cells from being damaged and starting a thermal runaway event.
The batteries are installed low down in the car, which lessens the possibility of being damaged in a collision.
The 3rd Measure is the Automatic Disconnection of the Battery
If an impact or excessive heat is detected, the battery is automatically disconnected from the system and switched off.
The feature is intended to prevent a thermal runaway event.
The 4th Measure is the Ongoing Testing of the Vehicle.
Apart from the internal product development and safety activities, Teslas are subjected to the Euro NCAP assessment; apart from protecting the passenger, the rating also tests the battery’s integrity after the car is involved in an accident.
The 5th Measure is the Heat Generated During Recharge
As a cell overheating can cause a runaway thermal event, all the processes are designed to keep heat variation under 10%.
To limit the battery’s temperature and rise to less than 10°C during the recharge, the available charging current is carefully monitored and electronically controlled by the Tesla battery recharge system.
If the temperature exceeds allowable ranges, the battery recharger stops the recharge.
Conclusion
The relatively few Tesla fires that have started through battery issues are infrequent. The chance of being involved in a fire in a Tesla is 2,546 times less than in a car powered by an internal combustion engine.
The press and social media like to blow the problem out of all proportion by using dramatic visuals and describing the harrowing experiences of affected Tesla owners. The reality is that there is a very much higher probability of this happening in a conventional car.
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.